Publications
Selected Papers
Govek KW*, Chen S*, Sgourdou P, Yao Y, Woodhouse S, Chen T, Fuccillo M, Epstein DJ’, Camara PG’. Developmental trajectories of thalamic progenitors revealed by single-cell transcriptome profiling and Shh perturbation. Cell Reports 41: 6 December 2022. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111768 [*authors contributed equally]. [‘corresponding authors].
In this paper, we applied longitudinal single cell RNA sequencing and regional abrogation of Sonic hedgehog (Shh), to map the developmental trajectories of thalamic progenitors, intermediate progenitors, and post-mitotic neurons as they coalesce into distinct thalamic nuclei. These results reveal key principles of thalamic development and provide mechanistic insights into neurodevelopmental disorders resulting from thalamic dysfunction.
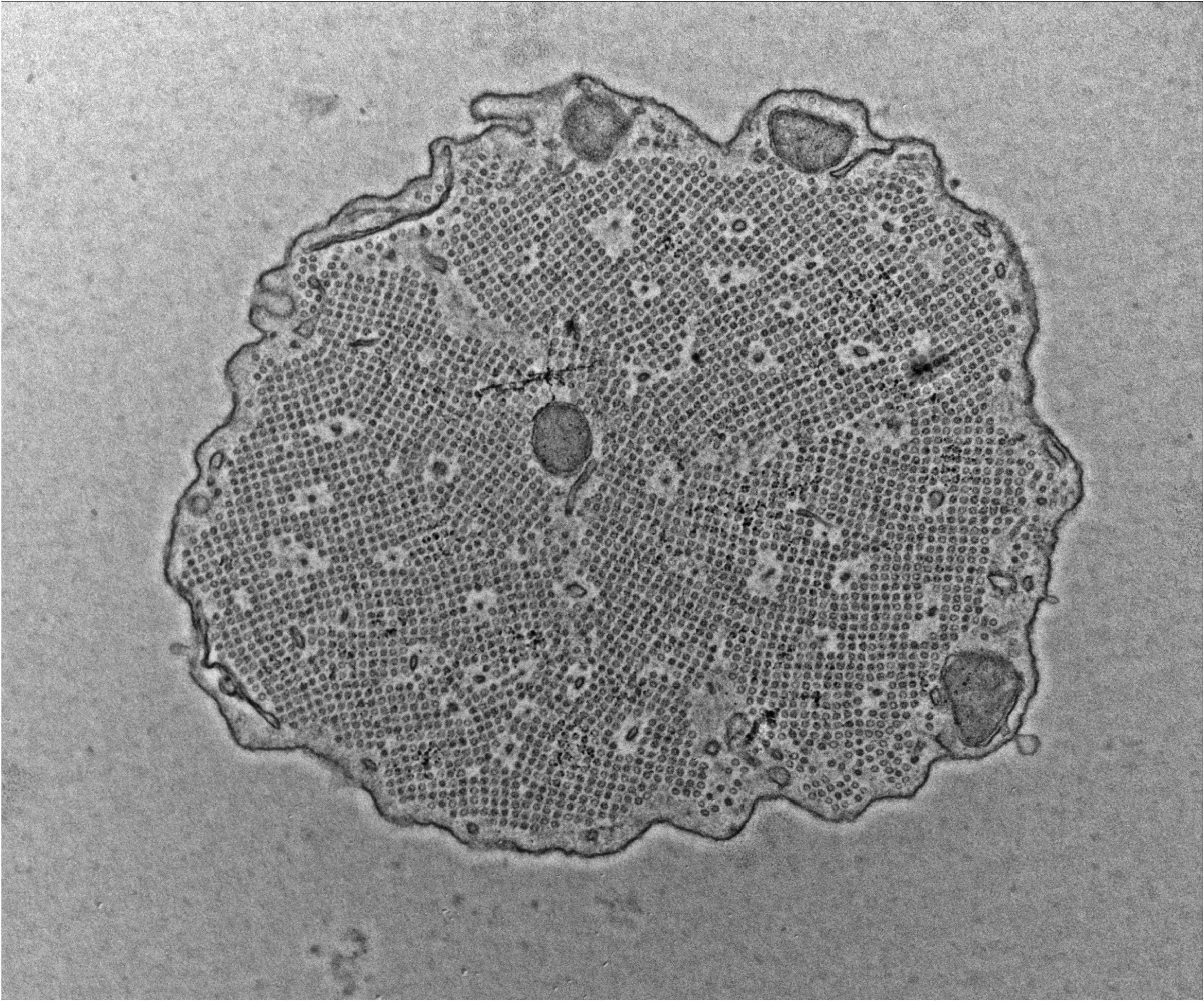
Chen T, Rohacek AM, Caporizzo M, Nankali A, Smits JJ, Oostrik J, Lanting CP, Kücük E, Gilissen C, van de Kamp JM, Pennings RJE, Rakowiecki SM, Kaestner KH, Ohlemiller KK, Oghalai JS, Kremer H, Prosser BL, Epstein DJ.: Cochlear supporting cells require GAS2 for cytoskeletal architecture and hearing. Developmental Cell 56: 1526-1540, 2021. PMID: 33964205.
In this paper, we demonstrated that inner ear supporting cells provide a structural framework for transmitting sound energy along the cochlear duct. In particular, we proposed that the microtubule bundling activity of GAS2, encoding a cytoskeletal regulatory protein, imparts supporting cells with the mechanical properties required to transmit sound energy through the cochlea and allow for proper hearing.
Muthu, V., Rohacek A.M., Yao, Y., Rakowiecki,S.M., Brown, A.S., Zhao, Y.T, Myers, J., Won, K.J, Ramdas, S., Brown, C.D., Peterson, K.A., and Epstein, D.J.: Genomic architecture of Shh dependent cochlear morphogenesis. Development 146: dev181339, 2019. PMID: 31488567.
In this paper, we utilized an integrated genomic approach, including comparative transcriptome analysis and mapping of open chromatin. These datasets serve as useful entry points for deciphering Shh-dependent regulatory mechanisms involved in cochlear duct morphogenesis and establishment of its constituent cell types.
Corman, T.S., Bergendahl, S. and Epstein, D.J.: Distinct temporal requirements of Sonic hedgehog signaling in development of the tuberal hypothalamus. Development 145, 2018. PMID: 30291164.
Here, we used fate mapping and conditional deletion models in mice to define requirements for dynamic Shh activity at distinct developmental stages in the tuberal hypothalamus, a brain region with important homeostatic functions.
Rohacek AM, Bebee TW, Tilton RK, Radens CM, McDermott-Roe C, Peart N, Kaur M, Zaykaner M, Cieply B, Musunuru K, Barash Y, Germiller JA, Krantz ID, Carstens RP, Epstein DJ.: ESRP1 Mutations Cause Hearing Loss due to Defects in Alternative Splicing that Disrupt Cochlear Development. Developmental Cell 43: 318-331, 2017. PMID: 29107558.
In this paper, we performed whole-exome sequencing in individuals with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and identified pathogenic mutations in Epithelial Splicing-Regulatory Protein 1 (ESRP1). Our findings here implicate mutations in ESRP1 as a cause of SNHL and demonstrate the complex interplay between alternative splicing, inner ear development, and auditory function.
Kahn, B.M., Corman, T.S., Lovelace, K., Hong, M., Krauss, R.S. and Epstein, D.J. : Prenatal ethanol exposure in mice phenocopies Cdon mutation by impeding Shh function in the etiology of optic nerve hypoplasia. Disease Models and Mechanisms 10: 29-37, 2017. PMID: 27935818.
Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD) is a congenital disorder characterized by optic nerve, pituitary and midline brain malformations. Here, we presented a model whereby mutations in Cdon, a Sonic hedgehog (Shh) co-receptor, and prenatal ethanol exposure increase SOD risk through spatiotemporal perturbations in Shh signaling activity.
Yao, Y., Minor, P.J., Zhao, Y-T., Jeong, Y., Pani, A.M. King, A.N., Symmons, O., Gan, L., Cardoso, W.V., Spitz, F., Lowe, C.J. and Epstein, D.J.: Cis-regulatory architecture of a brain-signaling center predates the origin of chordates. Nature Genetics 48: 575-580, 2016. PMID: 27064252.
Here, we systematically decoded a set of brain enhancers active in the zona limitans intrathalamica (zli), a signaling center essential for vertebrate forebrain development via the secreted morphogen Sonic hedgehog (Shh). These findings supported a strategy for delineating functionally conserved enhancers in the absence of overt sequence homologies and over extensive evolutionary distances.